Is Diabetes Treatments
Living with diabetes can be a complex and challenging journey, both for individuals diagnosed with the condition and their loved ones. With the ever-increasing prevalence of diabetes worldwide, it has become crucial to have a comprehensive understanding of effective treatments and practical tips for managing the disease. In this article, we explore various aspects of diabetes treatments, offering valuable insights and advice to not only those living with diabetes but also their support system of family and friends. From exploring the latest advancements in medication to discussing lifestyle modifications and holistic approaches, we dive into the vast and ever-evolving world of diabetes management. Whether you are seeking guidance for yourself or wanting to be a source of support for someone living with diabetes, this article aims to equip you with the knowledge and tools needed to navigate this challenging condition with confidence and resilience. So let’s embark on this journey together and gain a deeper understanding of the diverse options available when it comes to diabetes treatments.
Table of Contents
Overview of Diabetes Treatments
When it comes to managing diabetes, there are several treatment options available. These treatments aim to control blood sugar levels and minimize the complications associated with the condition. The three main categories of diabetes treatments include medications, insulin therapy, and lifestyle modifications. Each treatment option has its own benefits and considerations, and the choice of treatment often depends on the individual’s specific needs and preferences.
Medications for Diabetes
Medications play a crucial role in managing diabetes for many individuals. There are two main types of diabetes medications: oral medications and injectable medications. Oral medications are taken by mouth and help to lower blood sugar levels by various mechanisms. They can enhance insulin production, improve insulin sensitivity, or reduce glucose production in the liver. Injectable medications, on the other hand, are administered through injections and may include non-insulin injectables or insulin itself. These medications can help regulate blood sugar levels and may be prescribed depending on the type and severity of diabetes.
Some commonly prescribed medications for diabetes include metformin, sulfonylureas, meglitinides, DPP-4 inhibitors, GLP-1 receptor agonists, SGLT2 inhibitors, and insulin. These medications have different modes of action and are often prescribed in combination to achieve optimal blood sugar control. It is important to note that medication alone may not be sufficient to manage diabetes effectively, and it is often used alongside other treatment modalities.
Insulin Therapy
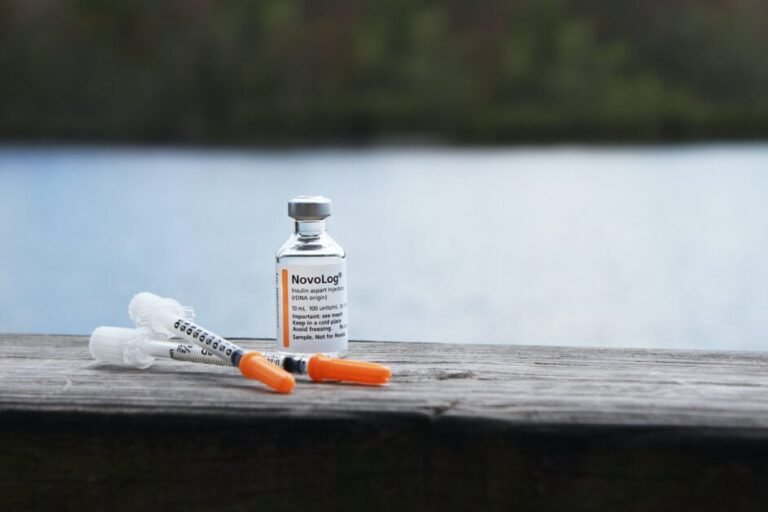
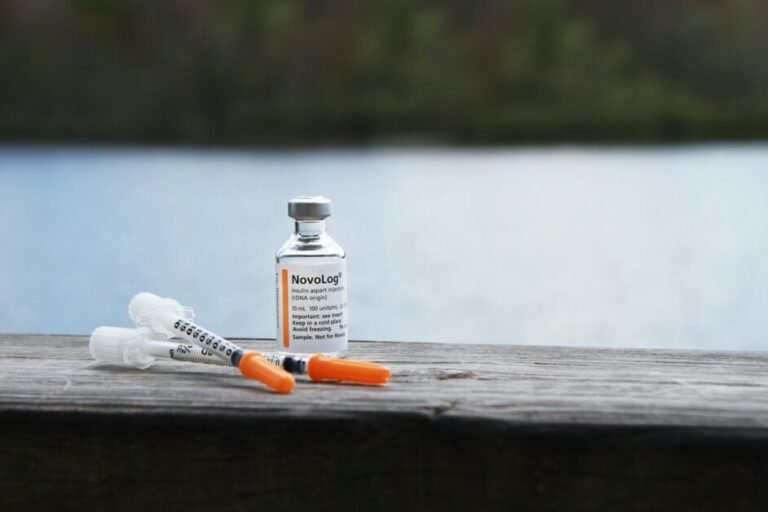
Insulin therapy is essential for individuals with type 1 diabetes and may also be prescribed for those with type 2 diabetes who cannot adequately control their blood sugar levels with other medications. Insulin is a hormone that helps regulate blood sugar by allowing glucose to enter cells for energy. There are different types of insulin available, including rapid-acting, short-acting, intermediate-acting, and long-acting insulin. The choice of insulin depends on factors such as mealtime needs, blood sugar control goals, and individual preferences.
Insulin can be administered through various delivery methods, including insulin pens, insulin pumps, and insulin syringes. These devices allow for more precise dosing and convenient administration. It is important for individuals on insulin therapy to understand how to properly administer insulin and monitor their blood sugar levels to achieve optimal control. Regular blood sugar monitoring is crucial for adjusting insulin doses and preventing hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia.
Lifestyle Modifications
In addition to medications and insulin therapy, lifestyle modifications are an integral part of managing diabetes. Making healthy lifestyle choices can have a significant impact on blood sugar control and overall well-being.
Dietary changes are an essential aspect of diabetes management. It is important to focus on a balanced diet that includes a variety of nutritious foods. Carbohydrate counting can be helpful in managing blood sugar levels, as carbohydrates have the most significant impact on blood sugar. Monitoring the glycemic index of foods can also provide guidance on their potential effects on blood sugar levels. Additionally, meal timing plays a role in managing diabetes by distributing food intake throughout the day and preventing large fluctuations in blood sugar levels.
Physical activity is another crucial lifestyle modification for individuals with diabetes. Regular exercise can improve insulin sensitivity, promote weight management, and help control blood sugar levels. Different types of exercise, such as aerobic activities, strength training, and flexibility exercises, offer various benefits. However, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional before starting an exercise program, as certain precautions may be necessary.
Weight management is vital for individuals with diabetes, as excess weight can worsen insulin resistance and blood sugar control. Setting realistic weight loss goals can help individuals achieve a healthier weight and improve their overall health. Additionally, maintaining a healthy weight through balanced eating and regular physical activity can help prevent the onset of type 2 diabetes and reduce the risk of complications in those already diagnosed.
Importance of Blood Sugar Monitoring
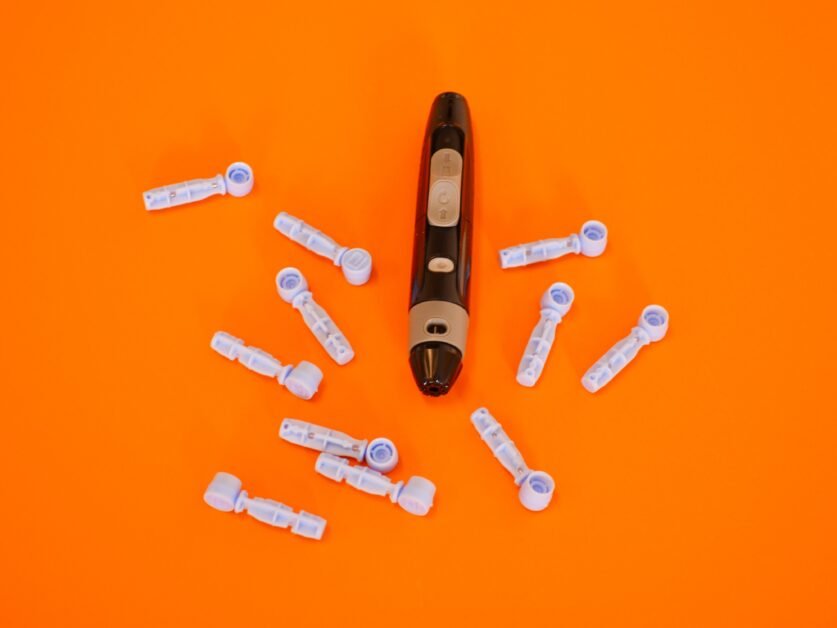
Monitoring blood sugar levels is a fundamental aspect of diabetes management. Regular blood sugar monitoring provides valuable information about how different factors, such as food, physical activity, medications, and stress, affect blood sugar levels. It allows individuals to make adjustments to their treatment plans and maintain optimal control.
Self-Monitoring of Blood Glucose (SMBG) involves using a portable blood glucose meter to measure blood sugar levels at specific times, such as before meals, after meals, and before bedtime. This practice helps individuals understand how their blood sugar levels fluctuate throughout the day and make necessary changes to their medication doses, dietary choices, or physical activity levels.
Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) is another method of monitoring blood sugar levels. This system uses a sensor inserted under the skin to continuously measure glucose levels in the interstitial fluid. The data is then transmitted to a receiver or smartphone, providing individuals with real-time information about their blood sugar levels and trends. CGM can be particularly useful for individuals who experience frequent fluctuations in blood sugar levels or have difficulty achieving stable control.
Diabetes and Meal Planning
Meal planning plays a crucial role in managing diabetes as it helps regulate blood sugar levels and maintain overall health. Several approaches can guide individuals in making appropriate food choices based on their specific needs and current blood sugar control goals.
Carbohydrate counting is a common method used in meal planning for diabetes. It involves estimating the number of carbohydrates in a meal or snack and adjusting insulin doses accordingly. This approach allows for flexibility in food choices while helping individuals maintain optimal blood sugar control.
The glycemic index (GI) is another tool that can be helpful in meal planning for diabetes. The GI ranks foods based on their potential to raise blood sugar levels. Choosing foods with a lower GI can help prevent sharp blood sugar spikes and promote more stable control. However, it is important to note that the GI does not take into account portion sizes, so it should be used in conjunction with other meal planning strategies.
Meal timing is an important consideration in diabetes management. It involves distributing food intake throughout the day to prevent large fluctuations in blood sugar levels. Spacing meals and snacks evenly can help individuals maintain stable blood sugar control and avoid excessive hunger or overeating.

Understanding Diabetic Diet
A balanced diabetic diet is essential for managing blood sugar levels and overall health. It focuses on consuming a variety of macronutrients in appropriate proportions while prioritizing nutrient-dense foods.
Balanced macronutrients, including carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, are essential for providing the body with energy and supporting various bodily functions. In meal planning for diabetes, it is important to consider the quality and quantity of each macronutrient. Carbohydrates, as mentioned earlier, have the most significant impact on blood sugar levels and should be consumed in appropriate portions. Proteins help build and repair tissues, while fats provide essential fatty acids and support hormone production. Choosing lean sources of protein and healthy fats, such as avocados, olive oil, and nuts, contributes to a well-rounded diabetic diet.
Fiber and whole grains are also essential components of a diabetic diet. Fiber helps regulate blood sugar levels, improve digestion, and promote satiety. Whole grains, such as whole wheat, brown rice, and quinoa, provide more nutrients and fiber compared to refined grains. Including these foods in the diet can help individuals maintain stable blood sugar levels and promote overall health.
Healthy fats, such as those found in fish, nuts, and seeds, are beneficial for individuals with diabetes. They can help improve heart health, decrease inflammation, and support insulin sensitivity. Incorporating these fats into the diet in moderation can be a wise choice for individuals managing diabetes.
Exercise and Diabetes
Regular exercise offers numerous benefits for individuals with diabetes. It can help improve insulin sensitivity, lower blood sugar levels, manage weight, and enhance overall well-being. Different types of exercise offer specific advantages, and it is important to find activities that are enjoyable and suitable for individual preferences and physical abilities.
Aerobic exercises, such as walking, cycling, swimming, and dancing, are particularly effective in managing diabetes. These activities increase heart rate and help burn calories, improving cardiovascular health and aiding in weight management. Additionally, aerobic exercises enhance insulin sensitivity, making the body more efficient at utilizing glucose for energy.
Strength training exercises are also beneficial for individuals with diabetes. These activities, such as weightlifting or using resistance bands, help build and maintain lean muscle mass. Improved muscle mass promotes better blood sugar control by increasing glucose uptake from the bloodstream.
Flexibility exercises, such as yoga or stretching routines, can help improve mobility, reduce muscle tension, and promote relaxation. Stress management through mindful movement practices can be particularly beneficial for individuals with diabetes, as stress can affect blood sugar levels.
Before starting an exercise program, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional, especially for individuals with certain medical conditions or complications. They can provide guidance on the suitable type, duration, and intensity of exercise and address any precautions specific to the individual’s health status.
Importance of Weight Management
Weight management is a crucial aspect of diabetes care. Excess weight, especially abdominal obesity, is closely linked to insulin resistance and poor blood sugar control in individuals with diabetes. Achieving a healthy weight and maintaining it can significantly improve overall health outcomes and reduce the risk of complications.
Setting realistic weight loss goals is important for individuals who are overweight or obese. Losing as little as 5-10% of body weight can have substantial health benefits and improve blood sugar control. It is essential to approach weight loss with a balanced and sustainable mindset, focusing on long-term lifestyle changes rather than quick fixes.
Maintaining a healthy weight is equally important for individuals who have already achieved their weight loss goals. Regular physical activity, a balanced diet, and mindful eating practices can help prevent weight regain and promote weight maintenance. It is important to remember that weight management is a lifelong endeavor and requires ongoing commitment to healthy habits.
Obesity and diabetes are closely intertwined. Excess weight can contribute to the development of type 2 diabetes and worsen the progression of the condition. Obesity increases insulin resistance, putting additional strain on the body’s insulin-producing cells. This leads to higher blood sugar levels and a greater risk of diabetes-related complications, such as heart disease, stroke, and nerve damage. By managing weight effectively, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of complications and improve their overall quality of life.
Alternative Treatments for Diabetes
In addition to conventional medical treatments, some individuals with diabetes may explore alternative therapies to complement their diabetes management. It is important to note that alternative treatments should never replace prescribed medications or lifestyle modifications. They should be approached with caution, and individuals should consult with their healthcare team before incorporating them into their treatment plans.
Herbal supplements, such as bitter melon, cinnamon, and fenugreek, have been studied for their potential blood sugar-lowering effects. However, the evidence supporting their efficacy is limited, and their effects can vary widely among individuals. It is crucial to discuss the use of herbal supplements with a healthcare professional to ensure safety and avoid potential interactions with medications.
Acupuncture is another alternative therapy that may be considered for diabetes management. This traditional Chinese medicine practice involves inserting thin needles into specific points on the body to balance energy flow. Some studies suggest that acupuncture may help improve blood sugar control and reduce diabetes-related symptoms. However, more research is needed to establish its effectiveness and better understand the mechanisms behind its potential benefits.
Biofield therapies, such as reiki and healing touch, focus on balancing the body’s energy fields to promote healing and well-being. While these therapies may offer relaxation and stress relief, there is limited scientific evidence supporting their direct impact on blood sugar control or diabetes management. It is important to approach biofield therapies as complementary rather than primary treatments for diabetes.
In conclusion, managing diabetes involves a comprehensive approach that includes medications, insulin therapy, lifestyle modifications, and potentially alternative treatments. Each individual’s treatment plan will vary based on their specific needs, preferences, and the guidance of their healthcare team. By combining these different approaches, individuals can effectively control their blood sugar levels, minimize complications, and improve their quality of life.