Type 2 Diabetes Tips And Tricks
Living with type 2 diabetes can be challenging, but with the right tips and tricks, managing the condition can become a little easier. Whether you are personally navigating the complexities of diabetes or supporting a loved one, this article aims to provide you with valuable advice and insights. From practical lifestyle changes to effective strategies for blood sugar control, we delve into the world of type 2 diabetes and equip you with the knowledge to make informed decisions for a healthier and happier life.

Table of Contents
Diet and Nutrition Tips
Developing a Healthy Meal Plan
When managing type 2 diabetes, it is important to develop a healthy meal plan that supports stable blood sugar levels and overall well-being. A balanced diet should include a variety of nutrient-dense foods from all food groups. Aim to consume a mix of carbohydrates, proteins, and healthy fats throughout the day. Including plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and low-fat dairy products can help provide essential nutrients while keeping your blood sugar levels in check.
Monitoring Carbohydrate Intake
Carbohydrates have the most significant impact on blood sugar levels, making it crucial to monitor your carbohydrate intake. Instead of completely avoiding carbohydrates, focus on consuming complex carbs that are rich in fiber, such as whole grains, legumes, and vegetables. These foods have a slower digestion rate, causing a gradual increase in blood sugar levels. Be mindful of portion sizes and try to spread your carbohydrate consumption over the course of the day to maintain stable blood sugar levels.
Choosing Low-Glycemic Index Foods
The glycemic index (GI) is a scale that ranks foods based on how quickly they raise blood sugar levels. Opting for low-GI foods can help manage blood sugar levels more effectively. Foods with a low GI score (55 or less) include most non-starchy vegetables, legumes, and whole grains. High-GI foods (70 or higher), such as white bread, sugary cereals, and processed snacks, should be limited. Choosing low-GI foods helps prevent blood sugar spikes and provides a steady source of energy.
Including Fiber-Rich Foods
Fiber is an essential component of a diabetes-friendly diet. It not only aids digestion but also helps regulate blood sugar levels and promotes heart health. Incorporating fiber-rich foods into your meals can help you feel fuller for longer and prevent overeating. Some excellent sources of fiber include fruits, vegetables, whole grains, beans, and nuts. Aim to consume at least 25-30 grams of fiber per day to maintain optimal health.
Limiting the Consumption of Sugary Beverages
Sugary beverages, such as soda, fruit juice, and sweetened tea, can cause a rapid spike in blood sugar levels due to their high sugar content. It is best to limit or avoid these drinks altogether. Instead, choose hydrating options such as water, unsweetened tea, or sparkling water with a squeeze of lemon or lime. If you crave a sweet beverage, opt for artificially sweetened options or naturally flavored water without added sugars.
Opting for Healthy Fats
Contrary to popular belief, not all fats are bad for you. In fact, including healthy fats in your diet can help improve heart health and manage blood sugar levels. Healthy fats are found in foods such as avocados, nuts, seeds, olive oil, and fatty fish like salmon. These fats can help you feel satisfied for longer and contribute to a well-rounded and nutritious meal plan.
Planning Portion Sizes
Portion control plays a crucial role in managing blood sugar levels and weight. It is essential to be mindful of how much you eat to prevent overconsumption of calories and carbohydrates. Using measuring cups, a food scale, or visual cues, such as using your hand as a guide, can help you estimate appropriate portion sizes. Be aware of serving sizes and adjust accordingly to ensure a balanced and controlled intake of nutrients.
Snacking Strategies
Snacking can be a part of a healthy meal plan, especially for individuals with type 2 diabetes. However, it is important to choose snacks carefully and monitor portion sizes. Opt for nutritious snacks that offer a combination of protein, fiber, and healthy fats. Some examples include Greek yogurt with berries, carrot sticks with hummus, a handful of almonds, or a small apple with peanut butter. Avoid sugary or processed snacks that can cause blood sugar spikes and provide empty calories.
Exercise and Physical Activity
Regular Aerobic Exercise
Engaging in regular aerobic exercise is highly beneficial for individuals with type 2 diabetes. Aerobic exercises, such as walking, jogging, cycling, swimming, or dancing, help improve cardiovascular health, lower blood sugar levels, and enhance insulin sensitivity. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise per week or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity exercise. Break it down into manageable sessions throughout the week and find activities that you enjoy to stay motivated.
Strength Training
In addition to aerobic exercise, incorporating strength training into your fitness routine has numerous benefits for individuals with type 2 diabetes. Strength training exercises, such as lifting weights, using resistance bands, or performing bodyweight exercises, help build and maintain muscle mass, improve insulin sensitivity, and increase overall strength. Aim for two to three sessions per week, targeting all major muscle groups. Start with lighter weights and progress gradually to avoid injury.
Incorporating Physical Activity into Daily Routine
In addition to dedicated exercise sessions, finding ways to incorporate physical activity into your daily routine can greatly contribute to managing type 2 diabetes. Simple lifestyle changes, such as taking the stairs instead of the elevator, parking farther away from your destination, or walking instead of driving short distances, can all add up and help increase your overall activity level. Every step counts, so find opportunities throughout the day to move your body.
Finding Enjoyable Exercises
To maintain consistency in your exercise routine, it is essential to find activities that you enjoy. Experiment with different forms of exercise to discover what suits your preferences and fits into your lifestyle. Whether it’s dancing, swimming, gardening, cycling, or playing a sport, the key is to engage in activities that bring you joy. By enjoying the exercise, you are more likely to stick with it and make physical activity a regular part of your life.
Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels During Exercise
When engaging in physical activity, it is important to monitor your blood sugar levels to ensure they stay within a safe range. Before exercising, check your blood sugar levels to establish a baseline. If your levels are too high or too low, it may not be safe to exercise. During exercise, keep a source of glucose, such as glucose tablets or a small snack, readily available in case your blood sugar drops. Afterward, check your levels again to determine how exercise affects your blood sugar.
Consulting a Health Professional Before Starting New Exercise Regimens
Before starting any new exercise regimen, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional, especially if you have underlying health conditions or concerns. Your doctor or a diabetes specialist can provide personalized guidance and help you determine the most suitable exercise plan for your specific needs and goals. They can also provide valuable advice on how to monitor your blood sugar levels and adjust medications as needed.
Blood Sugar Monitoring and Management
Regular Blood Sugar Testing
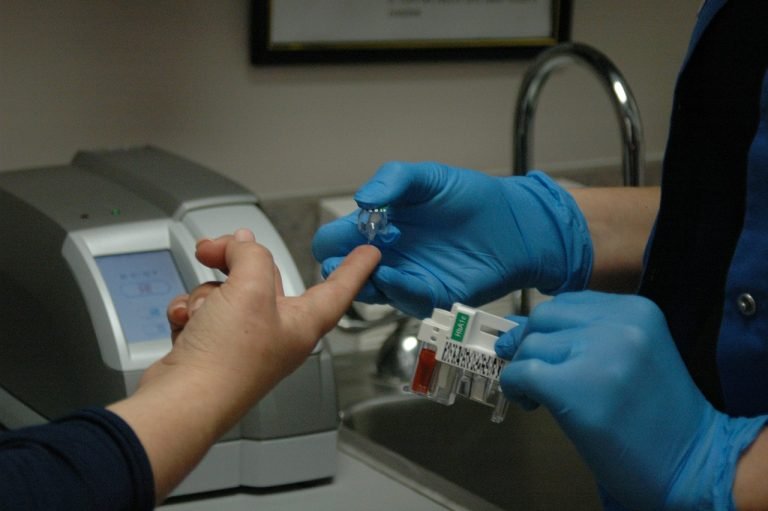
Regular blood sugar testing is essential for effectively managing type 2 diabetes. Monitoring your blood sugar levels allows you to track how food, physical activity, medications, and other factors impact your glucose levels. It enables you to make informed decisions about your diet, exercise routine, and medication management. Follow your healthcare team’s recommendations on how often to test your blood sugar and keep a record of the results.
Understanding Blood Sugar Targets
Understanding your blood sugar targets is crucial for managing type 2 diabetes. These targets indicate the desired range within which your blood sugar levels should typically fall. Your healthcare team will help you determine specific targets based on factors such as your age, overall health, and diabetes management goals. Knowing your targets allows you to take appropriate actions to keep your blood sugar levels within the recommended range and prevent complications.
Using a Glucose Meter
A glucose meter is a valuable tool for monitoring blood sugar levels at home. It allows you to obtain real-time information about your glucose levels and make necessary adjustments to your diet, exercise, or medication. Follow the instructions provided with your glucose meter to accurately measure your blood sugar. It is also important to regularly calibrate and maintain your meter to ensure accurate readings.
Keeping a Blood Sugar Log
Keeping a blood sugar log or journal is a helpful practice for individuals with type 2 diabetes. Recording your blood sugar levels, along with details about your meals, physical activity, medications, and other factors, can provide valuable insights into your diabetes management. It helps you identify patterns, track progress, and spot any potential issues. Share your log with your healthcare team during check-ups to facilitate collaborative decision-making and adjustments to your treatment plan.
Medication Compliance
Proper adherence to medication prescribed by your healthcare team is essential for effective blood sugar management. Take your medications as directed, and if you have trouble remembering, consider setting reminders or using pill organizers. Avoid skipping doses or making any changes to your medication regimen without consulting your healthcare provider. Adhering to your prescribed medication schedule helps maintain stable blood sugar levels and reduces the risk of complications.
Managing High Blood Sugar Levels
Sometimes, despite your best efforts, your blood sugar levels may spike above the desired range. When this happens, it is crucial to take necessary actions to bring your levels back down. Stay hydrated, engage in physical activity, and follow a balanced meal plan with a focus on low-GI foods and portion control. If your blood sugar remains consistently high, inform your healthcare team so they can adjust your treatment plan accordingly.
Addressing Low Blood Sugar Levels
Low blood sugar, also known as hypoglycemia, can occur when your blood sugar levels drop below the desired range. It is important to recognize the symptoms of low blood sugar, such as dizziness, confusion, sweating, and irritability, and take immediate action to raise your blood sugar levels. Consume a rapid-acting carbohydrate, such as fruit juice, glucose tablets, or a small piece of candy. Follow up with a protein and carbohydrate-containing snack to maintain stable blood sugar levels.
Stress Management Strategies
Identifying Sources of Stress
Stress can significantly impact blood sugar levels and overall well-being. Identifying the sources of stress in your life is the first step toward managing it effectively. Recognize situations, events, or people that trigger stress for you. It could be work-related pressures, family issues, financial concerns, or even chronic health conditions. Understanding the root causes of stress can help you develop strategies to cope with it more effectively.
Developing Coping Mechanisms
Once you have identified sources of stress, it is important to develop healthy coping mechanisms. Experiment with different strategies to find what works best for you. This could include engaging in hobbies, practicing deep breathing or meditation, journaling, listening to calming music, or seeking support from loved ones. Coping mechanisms help redirect your focus, reduce anxiety, and promote a sense of calm.
Practicing Relaxation Techniques
Relaxation techniques are effective in managing stress and promoting overall well-being. Deep breathing exercises, progressive muscle relaxation, and guided imagery are just a few examples of relaxation techniques that can help reduce stress levels. Incorporate these techniques into your daily routine, especially during moments of heightened stress or as part of a regular self-care practice.
Engaging in Stress-Relieving Activities
Engaging in activities that reduce stress levels and provide a sense of relaxation can significantly improve your overall well-being. Find activities that you enjoy and that help you unwind. This could include taking a bath, going for a walk in nature, practicing yoga or tai chi, reading a book, or listening to soothing music. An activity that brings you joy and helps you disconnect from stress can have a positive impact on both your mental and physical health.
Seeking Support from Family and Friends
Social support is a powerful tool for managing stress. Reach out to your family and friends and share your concerns or frustrations. Having someone to listen, offer comfort, or provide practical assistance can make a tremendous difference in managing stress levels. Surround yourself with a supportive network of people who understand and empathize with your experiences.
Considering Professional Support
Sometimes, managing stress on your own may not be enough. If stress becomes overwhelming or starts to affect your daily life, considering professional support can be beneficial. Therapists, counselors, or psychologists experienced in stress management can provide valuable guidance and strategies tailored to your specific needs. They can help you develop coping mechanisms, address underlying emotional challenges, and provide a safe space for you to express your feelings.
Healthcare Team and Regular Check-Ups
Building a Supportive Healthcare Team
Building a supportive healthcare team is essential for managing type 2 diabetes effectively. Seek out healthcare professionals who specialize in diabetes care and have experience working with individuals with your specific needs and goals. A diabetes educator, a registered dietitian, an endocrinologist, or a primary care physician can all contribute to your diabetes management and provide valuable guidance and support.
Regular Visits to Doctors and Specialists
Regular check-ups with your healthcare team are critical for monitoring your diabetes management and overall health. Schedule routine visits with your primary care physician and any specialists involved in your diabetes care, such as an endocrinologist, ophthalmologist, or podiatrist. These appointments allow for ongoing assessment of your blood sugar control, medications, potential complications, and the adjustment of your treatment plan if necessary.
Understanding Diabetes Medications
Understanding your diabetes medications is important for effective management. Familiarize yourself with the different types of medications prescribed for type 2 diabetes, including oral medications and insulin. Learn about their mechanism of action, proper dosage, and potential side effects. Ask your healthcare provider any questions you may have to ensure that you are taking your medications correctly and maximizing their benefits.
Monitoring Cholesterol and Blood Pressure
Diabetes is often associated with an increased risk of high cholesterol and high blood pressure, which can further contribute to cardiovascular complications. Monitoring and managing these conditions is crucial. Regularly check your cholesterol and blood pressure levels as recommended by your healthcare team. Follow a heart-healthy diet, engage in regular physical activity, and if necessary, take prescribed medications to keep these parameters within the desired range.
Routine Eye and Foot Examinations
People with type 2 diabetes are at an increased risk of developing eye and foot complications. Routine eye examinations, conducted by an ophthalmologist or optometrist, help detect early signs of diabetic retinopathy or other eye-related conditions. Additionally, regular foot examinations, preferably performed by a podiatrist, assist in identifying any changes in foot health that may require intervention. Early detection and timely treatment can help prevent long-term complications and maintain good overall health.
Importance of Vaccinations
Vaccinations play a vital role in protecting individuals with diabetes against preventable illnesses. Ensure that your immunizations are up to date, including vaccinations for influenza, pneumonia, and other recommended vaccines based on your age and individual circumstances. These vaccinations can help reduce the risk of complications and hospitalization associated with certain infections, especially during periods of seasonal outbreaks or pandemics.
Sleep and Diabetes
Maintaining a Consistent Sleep Schedule
Getting sufficient, quality sleep on a consistent basis is crucial for managing type 2 diabetes. Strive for a regular sleep schedule by going to bed and waking up at the same time each day, even on weekends. This helps regulate your body’s internal clock and promotes better sleep quality. Establishing a bedtime routine can also signal to your body that it is time to wind down and prepare for sleep.
Creating a Relaxing Bedtime Routine
Creating a relaxing bedtime routine can contribute to better sleep quality. Engage in activities that help you relax and unwind before bed. This could include reading a book, taking a warm bath, practicing yoga or meditation, or listening to soothing music. Avoid stimulating activities or exposure to bright lights, such as watching TV or using electronic devices, at least an hour before bed as they can interfere with your sleep-wake cycle.
Avoiding Stimulants Before Bed
Stimulants, such as caffeine and nicotine, can disrupt your sleep. Avoid consuming caffeinated beverages, like coffee or energy drinks, late in the day as they can keep you awake. Similarly, nicotine is a stimulant and can make it harder to fall asleep. Limit or avoid both caffeine and nicotine to promote better sleep quality.
Creating a Sleep-Friendly Environment
The environment in which you sleep can greatly impact the quality of your sleep. Create a sleep-friendly environment by making your bedroom comfortable, quiet, and dark. Invest in a supportive mattress and pillows, use blackout curtains or eye shades to block out any light, and keep the room at a temperature that feels comfortable for you. Minimize noise disturbances and consider using a white noise machine or earplugs if needed.
Managing Sleep Disorders
Sleep disorders, such as sleep apnea or insomnia, can be prevalent in individuals with type 2 diabetes. If you suspect you have a sleep disorder, consult with a healthcare professional who specializes in sleep medicine. They can conduct a thorough evaluation and recommend appropriate interventions or treatments to help you manage your sleep disorder effectively.
Seeking Professional Guidance for Sleep Issues
If you are experiencing persistent sleep issues that affect your daily life and overall well-being, seeking professional guidance can be beneficial. Sleep specialists can conduct sleep studies, offer behavioral therapy, or prescribe medications, if necessary, to help you address your specific sleep concerns. They can provide personalized strategies to improve your sleep quality, enhance daytime alertness, and support your overall health.

Educating Yourself and Supportive Resources
Attending Diabetes Education Classes
Attending diabetes education classes can provide valuable insights and skills to manage type 2 diabetes effectively. These classes, usually led by certified diabetes educators, provide comprehensive information about diabetes management, including meal planning, blood sugar monitoring, medication management, and lifestyle changes. They also offer a supportive environment for individuals with diabetes to connect and learn from one another.
Learning about Diabetes Management
Continuously educating yourself about diabetes management is essential for long-term success. Stay informed about the latest research, guidelines, and best practices related to managing type 2 diabetes. Read reputable sources, such as diabetes-focused websites, books, or magazines, and consult with your healthcare team to address any specific questions or concerns. Knowledge is a powerful tool in effectively managing your diabetes.
Utilizing Online Resources
The internet provides a wealth of information and resources for individuals with type 2 diabetes. Online platforms, such as reputable websites, blogs, and forums, can offer valuable insights, practical tips, and emotional support. However, be cautious when sourcing information online and ensure that you rely on trustworthy and science-based resources. Consult with your healthcare team if you have any doubts or questions about the information you find online.
Joining Diabetes Support Groups
Joining a diabetes support group can be immensely helpful in managing the emotional aspects of living with type 2 diabetes. These groups provide a safe and understanding space to share experiences, exchange tips, and seek emotional support from others who truly understand your journey. Search for local support groups in your community or consider joining online support groups where you can connect with individuals facing similar challenges.
Seeking Help through Hotlines or Helplines
Sometimes, you may need immediate assistance or have urgent questions related to your diabetes management. Hotlines or helplines specifically dedicated to diabetes can provide timely support and guidance. Save the contact information for diabetes helplines or crisis hotlines to have them readily available whenever you need to reach out for assistance.
Engaging with Diabetes-related Social Media Communities
Social media platforms offer opportunities to connect with diabetes-related communities and access a wealth of information and support. Follow reputable diabetes organizations, experts, and influencers on platforms such as Twitter, Facebook, or Instagram. Engage in conversations, ask questions, and share your experiences. However, exercise caution and verify information before applying any recommendations. Social media should never replace professional medical advice.
Weight Management Strategies
Setting Realistic Weight Loss Goals
For individuals with type 2 diabetes who are overweight or obese, incorporating weight management strategies into their lifestyle can greatly benefit overall health and blood sugar control. Start by setting realistic weight loss goals that are achievable and sustainable. Aim to lose about 1-2 pounds per week, which is considered a safe and healthy rate of weight loss. Small, gradual changes are more likely to lead to long-term success.
Balancing Caloric Intake and Physical Activity
Weight management involves finding the right balance between caloric intake and physical activity. To lose weight, you need to create a calorie deficit by consuming fewer calories than you burn. A combination of a healthy, calorie-controlled diet and regular physical activity is key. Consult with a registered dietitian or healthcare professional to determine the appropriate caloric intake and exercise routines that align with your weight management goals.
Choosing Nutrient-Dense Foods
When focusing on weight management, it is important to choose nutrient-dense foods that provide essential vitamins, minerals, and fiber, while being relatively low in calories. Fill your plate with fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. These foods are often more filling and satisfying than processed, calorie-dense options. Be mindful of portion sizes and use strategies, such as eating slowly and practicing mindful eating, to prevent overeating.
Monitoring Portion Sizes
Portion control plays a significant role in weight management. It is important to be mindful of portion sizes to avoid consuming excess calories. Use measuring cups, a food scale, or visual cues to ensure appropriate portion sizes. Avoid eating directly from packages, as it can lead to mindless overeating. By practicing portion control, you can still enjoy a variety of foods while managing your weight effectively.
Combining Cardiovascular and Strength Training Exercises
To promote weight loss and maintain muscle mass, it is important to combine cardiovascular exercises with strength training exercises. Cardiovascular exercises, such as brisk walking, jogging, or cycling, help burn calories and improve cardiovascular health. Strength training exercises, such as weightlifting or bodyweight exercises, help build and maintain muscle mass, which can boost your metabolism and assist in weight management.
Seeking Professional Help for Weight Management
Managing weight can be challenging, especially when navigating the complexities of type 2 diabetes. If you are struggling with weight management or have specific concerns, seek professional help from a registered dietitian, weight management specialist, or healthcare provider experienced in diabetes care. They can provide personalized guidance, strategies, and ongoing support to help you achieve your weight management goals.
Managing Medications and Insulin
Taking Medications as Prescribed
Proper adherence to medications prescribed by your healthcare team is crucial for managing type 2 diabetes effectively. Take your medications as directed and at the recommended times. If you have trouble remembering, consider setting reminders, using pill organizers, or incorporating medications into your daily routine. If you have concerns or experience any side effects, discuss them with your healthcare provider before making any changes to your medication regimen.
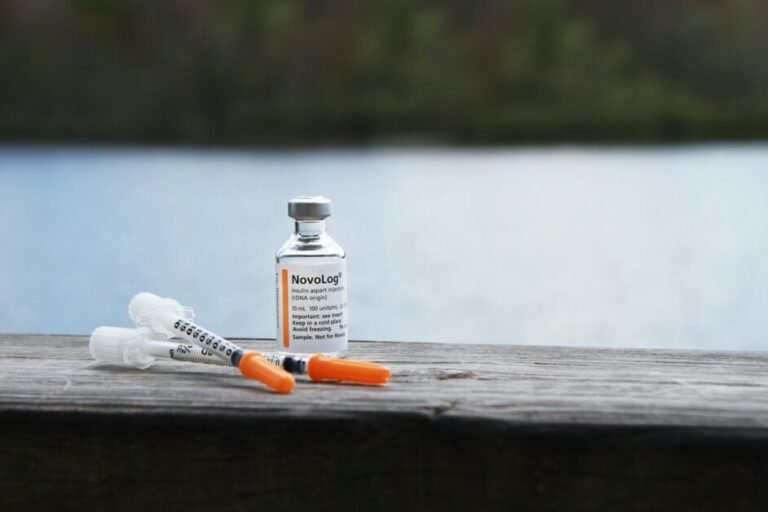
Understanding the Role of Insulin
Insulin is a hormone that helps regulate blood sugar levels. Some individuals with type 2 diabetes may require insulin therapy to achieve optimal blood sugar control. Understanding the role of insulin and its administration is important. Learn how to properly inject insulin, store it at the appropriate temperature, and manage any necessary adjustments to your insulin doses. Speak with your healthcare provider if you have any questions or concerns about insulin therapy.
Creating a Medication Schedule
Creating a medication schedule can help ensure that you take your medications as prescribed and at the recommended times. Consistency is key in managing your blood sugar levels effectively. Use tools such as pill organizers, smartphone alarms, or medication apps to help you organize and track your medications. Review your medication schedule regularly and adjust as needed.
Adhering to Proper Storage Recommendations
Proper storage of medications, especially insulin, is crucial to maintain their effectiveness. Follow the storage recommendations provided by the manufacturer or healthcare provider. Insulin should be stored in a cool place away from direct sunlight, extreme temperatures, and rapid temperature changes. Always check the expiration dates and dispose of any expired, damaged, or unusable medications properly.
Avoiding Drug Interactions
Be cautious of potential drug interactions when taking multiple medications, including over-the-counter medications, supplements, and herbal remedies. Some medications, when taken together, can interact and interfere with their effectiveness or lead to potential side effects. Inform your healthcare provider about all the medications and supplements you are taking to ensure that they are compatible and safe.
Managing Side Effects
Some diabetes medications may have side effects, which can vary from person to person. Common side effects include gastrointestinal discomfort, weight gain, or low blood sugar levels. It is important to be aware of the potential side effects and consult with your healthcare provider if you experience any unexpected or severe symptoms. They can assess your individual situation and make necessary adjustments to your medication to minimize side effects.
Discussing Medication Adjustments with Healthcare Providers
Over time, your medication needs may change, especially as your diabetes management progresses or if you experience any changes in your health status. It is important to regularly discuss your medication regimen with your healthcare provider during check-ups. Together, you can review your blood sugar control, assess the effectiveness of your current medication plan, and make any necessary adjustments or additions to optimize your diabetes management.
Emotional Well-being and Diabetes
Addressing Emotional Challenges of Diabetes
Managing a chronic condition like type 2 diabetes can often bring about emotional challenges. Addressing these challenges is important for overall well-being. Acknowledge any feelings of stress, frustration, or sadness that may arise from living with diabetes. Understand that it is normal to experience a range of emotions and that it is essential to prioritize your emotional health as much as your physical health.
Seeking Emotional Support
Don’t hesitate to seek emotional support when needed. Talk to your loved ones about your feelings, challenges, and concerns. Reach out to friends or family members who can provide a listening ear, empathy, and encouragement. If necessary, consider professional counseling or therapy to help process and navigate the emotional aspects of managing type 2 diabetes.
Engaging in Mindfulness Practices
Practicing mindfulness can help you develop awareness and acceptance of your thoughts and emotions, ultimately reducing stress and promoting emotional well-being. Incorporate mindfulness techniques into your daily routine, such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, or guided imagery. These practices can help you stay present, manage stress, and increase your resilience in dealing with the challenges of living with type 2 diabetes.
Prioritizing Self-Care
Engaging in self-care activities is crucial for maintaining emotional well-being while managing type 2 diabetes. Prioritize activities that bring you joy, relaxation, and fulfillment. This could include hobbies, physical activities, spending time in nature, reading, or engaging in creative pursuits. Taking time for yourself allows you to recharge, reduce stress, and enhance your overall quality of life.
Adopting a Positive Mindset
Maintaining a positive mindset can significantly impact your diabetes management journey. Embrace a positive outlook and focus on your accomplishments, no matter how small they may seem. Celebrate your progress and remind yourself of your resilience and ability to overcome challenges. A positive mindset can help you stay motivated, navigate difficult times, and approach your diabetes management with optimism.
Exploring Professional Therapy Options
If you find that emotional challenges associated with diabetes are significantly impacting your daily life, relationships, or overall well-being, consider seeking professional therapy. Therapists or counselors experienced in working with individuals with chronic conditions, such as diabetes, can offer guidance, coping strategies, and support tailored to your specific needs. Therapy sessions can provide a safe space to explore and address your emotional concerns effectively.
Managing type 2 diabetes requires a holistic approach, incorporating various strategies to ensure optimal health and well-being. By adopting a healthy meal plan, engaging in regular exercise, monitoring blood sugar levels, managing stress, building a supportive healthcare team, prioritizing sleep, seeking education and supportive resources, managing weight, effectively using medications, and addressing emotional well-being, you can successfully manage your diabetes and live a fulfilling life. Remember, you are not alone in your journey, and taking small steps each day towards a healthier lifestyle can make a significant difference in your overall health and quality of life.