Managing Sugar Intake for Diabetics
If you or someone you know has diabetes, managing sugar intake is crucial for maintaining a balanced and healthy lifestyle. Contrary to popular belief, diabetics are not completely restricted from consuming sugar. With the right knowledge and approach, it is possible for individuals with diabetes to enjoy a variety of foods while keeping their blood sugar levels in check. In this article, we will explore some helpful tips and advice for managing sugar intake for diabetics and provide valuable insights for both individuals with diabetes and their loved ones.
Table of Contents
Understanding Diabetes
Diabetes is a chronic medical condition that affects millions of people worldwide. There are primarily two types of diabetes: type 1 and type 2. type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease where the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas, leading to a complete lack of insulin production. On the other hand, type 2 diabetes is characterized by the body’s inability to properly utilize insulin or a decreased production of insulin.
Impact of Sugar on Diabetes
Sugar, particularly in the form of glucose, plays a significant role in diabetes management. When you consume sugary foods or beverages, your blood sugar levels rise. In individuals with diabetes, this increase can be especially problematic as the body struggles to regulate blood sugar. Consistently high blood sugar levels can lead to various complications, such as nerve damage, cardiovascular issues, and kidney problems.
Recommended Daily Sugar Intake for Diabetics
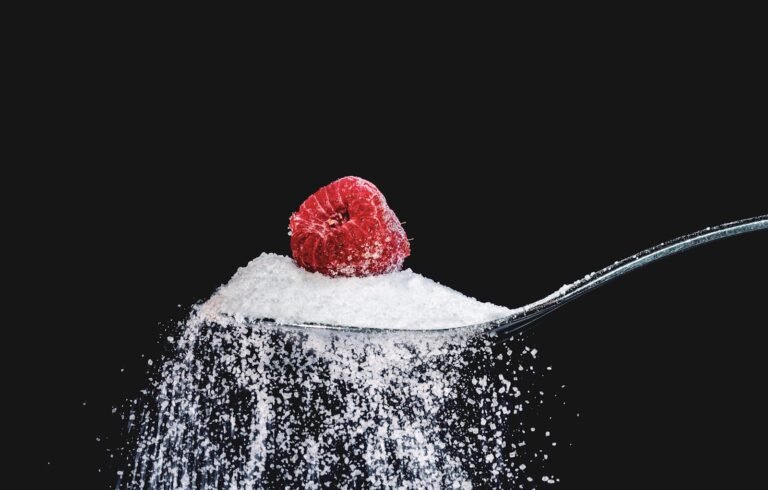
When it comes to sugar intake, it is essential for diabetics to closely monitor and regulate their consumption. The American Diabetes Association recommends that diabetics limit their daily added sugar intake to no more than 25 grams for women and 36 grams for men. It is important to note that this recommendation refers to added sugars and does not include naturally occurring sugars found in fruits and other whole foods.
Managing Sugar Intake
To effectively manage sugar intake as a diabetic, there are several strategies to implement. monitoring blood sugar levels regularly is crucial in determining how certain foods affect your body. By understanding your body’s response to different foods, you can make more informed choices. Reading food labels is also essential in identifying hidden sugars and making informed decisions about what you consume.
Limiting Added Sugars in Diet
One of the most effective ways to manage sugar intake is by limiting added sugars in your diet. Added sugars are those that are not naturally present in foods but are added during processing or preparation. Examples include table sugar, corn syrup, and high-fructose corn syrup. These added sugars provide little nutritional value and can lead to spikes in blood sugar levels. Instead, focus on a diet rich in whole, unprocessed foods that are lower in added sugars.
Choosing Low Glycemic Index Foods
The glycemic index (GI) is a tool that ranks food based on their effect on blood sugar levels. Foods with a high GI cause a rapid increase in blood sugar, while low GI foods have a more gradual impact. As a diabetic, it is beneficial to choose foods with a lower GI to help stabilize blood sugar levels. Whole grains, legumes, non-starchy vegetables, and lean proteins are generally lower on the glycemic index and can be great choices for individuals with diabetes.
Healthy Substitutes for Sugar
While it is important to limit sugar intake, it doesn’t mean you have to give up all sweetness in your diet. There are various healthy substitutes for sugar that can be used in moderation without significantly impacting blood sugar levels. Natural sweeteners such as honey, maple syrup, and dates can add a touch of sweetness to dishes without causing drastic spikes in blood sugar.
Artificial Sweeteners
Another option for those looking to reduce sugar intake is the use of artificial sweeteners. These are non-nutritive sweeteners that provide sweetness without adding calories or carbohydrates to the diet. Popular artificial sweeteners include aspartame, sucralose, and stevia. However, it is essential to note that while artificial sweeteners do not raise blood sugar levels, they may not be suitable for everyone, and excessive consumption should be avoided.
Health Benefits and Risks of Substitute Options
The use of substitute options for sugar can have both benefits and risks. Natural sweeteners like honey and maple syrup may contain trace amounts of vitamins and minerals, providing some nutritional value. However, they should still be consumed in moderation due to their overall impact on blood sugar levels. Artificial sweeteners, while not affecting blood sugar levels, may have side effects for some individuals, such as digestive issues or headaches. It is important to find a balance that works for you and consult with a healthcare professional if needed.

Meal Planning for Diabetics
Meal planning is a crucial aspect of managing diabetes and keeping blood sugar levels in check. Balancing carbohydrates and sugars is an essential component of creating well-rounded meals for individuals with diabetes. It is important to choose complex carbohydrates that are digested more slowly, causing a gradual increase in blood sugar levels.
Importance of Fiber-rich Foods
Including fiber-rich foods in your diet is highly beneficial for individuals with diabetes. Fiber helps regulate blood sugar levels by slowing down the absorption of glucose into the bloodstream. It also aids in digestion, promotes feelings of satiety, and can support weight management. Excellent sources of dietary fiber include whole grains, legumes, fruits, and vegetables.
Timing and Portion Control
Not only is the content of your meals important, but also when and how much you eat. Timing your meals and snacks can help maintain stable blood sugar levels throughout the day. It is recommended to have regular meals at consistent times and avoid long gaps between meals. Portion control is also vital to prevent overeating and maintain a healthy weight.
Creating Balanced Meals
To create well-balanced meals, it is essential to include a variety of food groups and macronutrients. Aim to include a source of lean protein, such as chicken, fish, or tofu, along with fiber-rich carbohydrates, like whole grains or legumes, and a generous portion of non-starchy vegetables. This combination provides a good balance of nutrients and helps maintain stable blood sugar levels.
Strategies for Sugar Consumption
While it is important to limit sugary treats, completely eliminating them from your diet is not necessary. Including sugary treats in moderation can still be part of a healthy lifestyle for individuals with diabetes.
Managing Stress and Emotional Eating
Stress can have a significant impact on blood sugar levels, as it triggers the release of hormones that can cause fluctuations. It is important for individuals with diabetes to find healthy coping mechanisms for stress and avoid turning to food for comfort. Engaging in stress reduction techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, or physical activity can help manage stress levels and reduce the urge for emotional eating.
Socializing and Eating Out
Social gatherings and eating out can present challenges for individuals with diabetes. It can be helpful to plan ahead by checking restaurant menus for healthier options or discussing dietary needs with hosts when attending events. Portion control and mindful eating techniques can also be useful in managing sugar intake during social situations.
Identifying Hidden Sugars in Foods
When managing sugar intake, it is crucial to be aware of hidden sugars in foods. Many packaged and processed foods contain added sugars that may not be immediately apparent. Reading food labels and familiarizing oneself with different names for sugar, such as sucrose, fructose, or maltose, can help in identifying and avoiding products high in added sugars.
The Role of Exercise
Physical activity plays a vital role in diabetes management. Regular exercise can help control blood sugar levels by increasing insulin sensitivity and improving the body’s ability to use glucose for energy. It is important to choose suitable exercises that align with your fitness level and take into consideration any pre-existing health conditions.

Choosing Suitable Exercises
Low-impact activities such as walking, swimming, and cycling are excellent choices for individuals with diabetes. These exercises are gentle on the joints while still providing cardiovascular benefits. Strength training exercises can also be beneficial as they help build and maintain muscle mass, which aids in glucose uptake and utilization.
Timing Exercise with Meals
Timing exercise with meals can have a positive impact on blood sugar control. Engaging in physical activity shortly after a meal can help lower blood sugar levels by promoting glucose uptake by muscles for energy. However, it is important to monitor blood sugar levels closely during and after exercise to prevent hypoglycemia.
Precautions and Recommendations
Before starting or modifying an exercise routine, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional or an exercise specialist. They can provide personalized recommendations based on your specific health condition and individual needs. It is also essential to stay hydrated during exercise and monitor blood sugar levels to ensure they remain within a safe range.
Maintaining a Healthy Lifestyle
In addition to managing sugar intake and incorporating exercise, maintaining a healthy lifestyle is key for individuals with diabetes.
Importance of Regular Sleep
Getting adequate sleep is essential for overall health and wellbeing, particularly for individuals with diabetes. Lack of sleep can influence blood sugar control and insulin sensitivity. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night to support your diabetes management efforts.
Staying Hydrated
Proper hydration is important for everyone, but it holds particular significance for individuals with diabetes. Drinking enough water helps maintain optimal blood sugar levels and supports overall health. Aim to drink at least 8 cups of water per day and adjust your intake based on activity level and climate.
Well-Balanced Diet
Adopting a well-balanced diet is crucial for individuals with diabetes. Emphasize whole, unprocessed foods and prioritize nutrient-dense choices. This includes consuming a variety of fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, whole grains, and healthy fats.
Regular Monitoring and Check-ups
Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels and routine check-ups with healthcare professionals are essential for effective diabetes management. Monitoring blood sugar allows for adjustments in diet, medication, or lifestyle as needed. Regular check-ups with your healthcare team help ensure that any potential issues are addressed promptly and that your diabetes management plan remains on track.
Mental Health and Diabetes
The impact of mental health on diabetes management should not be overlooked. Managing stress and anxiety, seeking emotional support, and implementing stress reduction techniques can have a significant positive impact on diabetes management.
Managing Stress and Anxiety
Stress and anxiety can affect blood sugar levels, making it important for individuals with diabetes to find healthy ways to manage these emotions. Techniques such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, and engaging in hobbies or activities that bring joy and relaxation can help reduce stress and promote overall wellbeing.
Seeking Emotional Support
Living with diabetes can be challenging, and it is important to seek emotional support when needed. This may come from loved ones, support groups, or mental health professionals who can provide guidance and understanding. Talking openly about your feelings and experiences can help reduce the emotional burden associated with the condition.
Impact of Mental Well-being on Diabetes Management
Mental well-being plays a crucial role in diabetes management. When you are in a positive state of mind, you are more likely to make healthier choices, stick to your diabetes management plan, and effectively manage stress levels. Prioritizing mental well-being can lead to better blood sugar control and overall health outcomes.
Implementing Stress Reduction Techniques
Implementing stress reduction techniques can help individuals with diabetes better manage their condition. Techniques such as yoga, meditation, regular exercise, and spending time in nature can have a calming effect on the mind and body. Find what works best for you and make it a regular part of your routine.
Educating Family and Friends
Involving your family and friends in your diabetes management journey can provide much-needed support and understanding.
Providing Information on Diabetes
Take the time to educate your family and friends about diabetes, its impact, and its management. Share information about healthy eating, exercise, and the importance of blood sugar control. By providing accurate information, you can foster a supportive and inclusive environment.
Supporting Dietary Changes
Encourage your loved ones to support your dietary changes by making healthier choices themselves. By including nutritious options in shared meals and snacks, they can be more accommodating and understanding of your needs.
Encouraging Physical Activity
Engage your family and friends in physical activities to promote an active lifestyle. This can be as simple as going for walks together, participating in sports or fitness classes, or exploring new outdoor activities. By making exercise a fun and shared experience, it becomes easier to maintain a consistent routine.
Creating a Supportive Environment
Creating a supportive environment is crucial for individuals with diabetes. Encourage open communication, understanding, and empathy among your family and friends. Provide opportunities for them to ask questions and address any concerns they may have about supporting your diabetes management.
Consulting Healthcare Professionals
Working closely with healthcare professionals is essential in effectively managing diabetes and making informed decisions about your health.
Importance of Regular Medical Appointments
Regular medical appointments with your primary care physician or endocrinologist are crucial for monitoring your diabetes and making adjustments to your management plan as needed. These appointments provide an opportunity to discuss any concerns, review blood sugar levels, and assess overall health.
Working with a Registered Dietitian
A registered dietitian specializing in diabetes can provide personalized guidance on meal planning, portion control, and managing sugar intake. They can help create a tailored nutrition plan that aligns with your specific dietary needs and health goals.
Collaborating with an Endocrinologist
Endocrinologists specialize in the treatment of hormonal disorders, including diabetes. Collaborating with an endocrinologist can provide a more in-depth understanding of your diabetes management plan and ensure that you receive specialized care and treatment options that best suit your needs.
Utilizing Diabetes Education Programs
Diabetes education programs offer valuable resources and support to individuals living with diabetes. These programs provide education on various aspects of diabetes management, including nutrition, exercise, medication management, and emotional well-being. Taking advantage of these programs can enhance your knowledge and empower you to take control of your diabetes.