Is Diabetes Treatment Permanent
Living with diabetes can be a lifelong challenge, and many individuals wonder if there is a permanent solution for treating this condition. In this article, we discuss the various treatments available for diabetes and provide tips and advice for both individuals with diabetes and their loved ones. So, if you’re looking for answers about whether diabetes treatment is permanent, keep reading to gain a deeper understanding of this topic.

Table of Contents
Overview of Diabetes
Diabetes is a chronic medical condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It occurs when the body is unable to properly regulate blood sugar levels. There are three main types of diabetes: type 1, type 2, and gestational diabetes. type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease in which the immune system attacks the cells in the pancreas that produce insulin. Type 2 diabetes is the most common form and is often associated with lifestyle factors such as poor diet and lack of exercise. Gestational diabetes occurs during pregnancy and usually resolves after childbirth.
Causes of Diabetes
The causes of diabetes vary depending on the type. For type 1 diabetes, the exact cause is unknown, but it is believed to be a combination of genetic and environmental factors. It is thought that certain viruses and infections may trigger the autoimmune response that leads to type 1 diabetes. Type 2 diabetes is primarily caused by a combination of genetic factors and lifestyle choices. Factors such as poor diet, sedentary lifestyle, obesity, and family history all play a role in the development of type 2 diabetes. Gestational diabetes is believed to be caused by hormonal changes that occur during pregnancy, which can affect the body’s ability to regulate blood sugar levels.
Diabetes Management
Managing diabetes is crucial for maintaining overall health and preventing complications. Diabetes management involves a combination of medication, diet, exercise, and lifestyle changes. It is important for individuals with diabetes to work closely with their healthcare team to develop a personalized management plan. This may include the use of oral medications or insulin injections to help regulate blood sugar levels. In addition, adopting a healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and making lifestyle changes such as weight management and stress reduction are all key components of diabetes management.
Medication for Diabetes
There are two main types of medication used to treat diabetes: oral medications and insulin injections. Oral medications are typically prescribed for individuals with type 2 diabetes and work by either increasing insulin production in the body or improving the body’s response to insulin. Some common oral medications for diabetes include metformin, sulfonylureas, and thiazolidinediones. Insulin injections, on the other hand, are primarily used for individuals with type 1 diabetes or those with type 2 diabetes who cannot adequately manage their blood sugar levels with oral medications alone. Insulin is injected subcutaneously and works by allowing glucose to enter the body’s cells, thus lowering blood sugar levels.

Diet and Exercise
Diet and exercise play a crucial role in managing diabetes effectively. Proper nutrition is key in maintaining stable blood sugar levels and preventing complications. It is important for individuals with diabetes to focus on consuming a balanced diet that includes foods high in fiber, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Avoiding sugary and processed foods is also important for blood sugar control. Regular exercise is equally important as it helps lower blood glucose levels and improves insulin sensitivity. Engaging in activities such as brisk walking, jogging, swimming, or cycling for at least 150 minutes per week can have significant benefits for individuals with diabetes.
Lifestyle Changes
In addition to medication, diet, and exercise, making certain lifestyle changes can greatly improve diabetes management. Weight management is particularly important, especially for individuals with type 2 diabetes. Losing excess weight can improve insulin sensitivity and reduce the need for medication. Stress management is also crucial, as stress hormones can affect blood sugar levels. Engaging in activities such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises can help reduce stress levels. Additionally, getting enough quality sleep is essential for individuals with diabetes, as sleep deprivation can affect insulin sensitivity and lead to imbalances in blood sugar levels.
Diabetes Complications
Diabetes can lead to a variety of complications if not properly managed. Long-term complications include heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, nerve damage, and eye problems. These complications can develop over time and are often the result of consistently high blood glucose levels. Short-term complications, on the other hand, can occur suddenly and include hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) and hyperglycemia (high blood sugar). It is important for individuals with diabetes to be aware of the signs and symptoms of these complications and seek medical attention if necessary.
Is Diabetes Curable?
While diabetes is a chronic condition that cannot be cured, it can be effectively managed. Understanding the disease and its underlying causes is crucial in developing an individualized treatment plan. Type 1 diabetes cannot be prevented or cured, and individuals with this type will require lifelong insulin therapy. However, type 2 diabetes can often be effectively managed through lifestyle changes such as diet and exercise, as well as medication if necessary. Current medical research is focused on finding new treatments and technologies that can help improve diabetes management and ultimately find a cure.
Diabetes Prediabetes Progression
Prediabetes is a condition in which blood sugar levels are higher than normal but not yet high enough to be classified as type 2 diabetes. It is estimated that over 88 million American adults have prediabetes, putting them at a higher risk of developing diabetes. However, it is important to note that prediabetes is not a guaranteed progression to type 2 diabetes. With lifestyle changes such as adopting a healthy diet, engaging in regular exercise, and losing excess weight, it is possible to prevent or delay the onset of type 2 diabetes.
Managing Diabetes Effectively
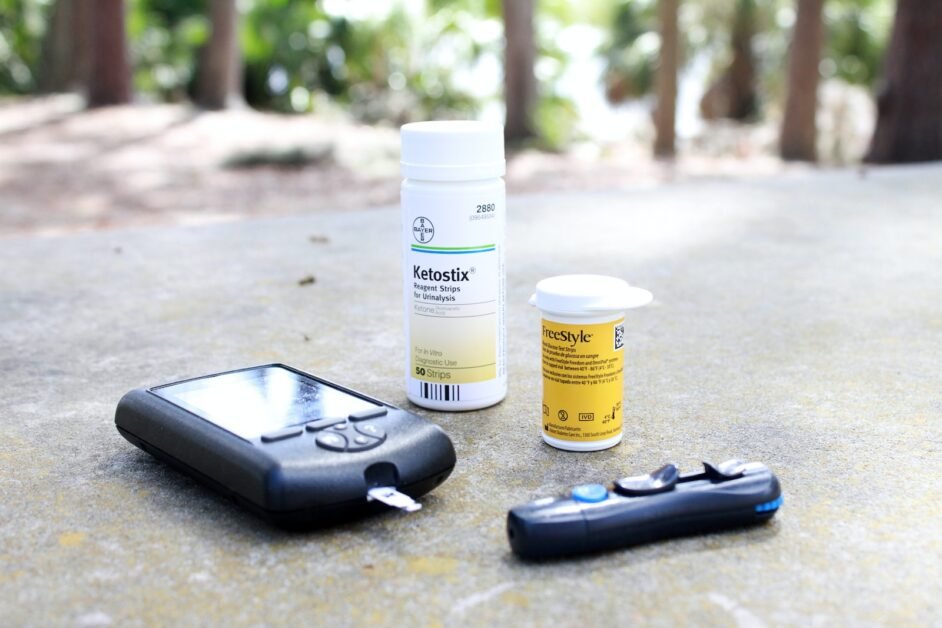
Managing diabetes effectively involves regular check-ups to monitor blood sugar levels, assess overall health, and adjust treatment plans if necessary. Regular check-ups allow healthcare professionals to catch any potential complications early and make necessary adjustments to medications or lifestyle recommendations. In addition, individuals with diabetes should monitor their blood glucose levels regularly using a glucometer. This helps to ensure that blood sugar levels are within the target range and allows for immediate intervention if levels become too high or too low.
Alternative Treatments
While medication, diet, exercise, and lifestyle changes are the mainstay of diabetes management, some individuals may explore alternative treatments. Herbal remedies, such as cinnamon or bitter melon, have been traditionally used in certain cultures to help regulate blood sugar levels. Acupuncture, a traditional Chinese medicine practice, has also been studied for its potential benefits in improving insulin sensitivity and blood sugar control. Additionally, some individuals may choose to take dietary supplements such as chromium or alpha-lipoic acid, although it is important to discuss these options with a healthcare professional before incorporating them into a treatment plan.
Conclusion
In conclusion, diabetes is a chronic condition that requires ongoing treatment and management to maintain stable blood sugar levels and prevent complications. With a combination of medication, diet, exercise, and lifestyle changes, individuals with diabetes can lead healthy and fulfilling lives. Ongoing research and advancements in the medical field provide hope for improved treatments and ultimately a cure for diabetes in the future. By taking proactive steps towards effective diabetes management, individuals can minimize the impact of this condition on their overall health and well-being.