Can diabetes complications be prevented?
Living with diabetes can often come with its fair share of concerns and potential complications, but is it possible to prevent these issues? Whether you personally have diabetes or have a loved one who does, it’s important to have a solid understanding of how to manage the condition effectively and minimize the risks of complications. In this article, I will provide helpful tips and advice aimed at both individuals with diabetes and their family and friends, highlighting the importance of proactive measures in keeping these complications at bay.
Table of Contents
Understanding Diabetes Complications
Diabetes complications refer to the various health issues that can arise as a result of uncontrolled diabetes. These complications can affect several parts of the body, including the heart, kidneys, eyes, nerves, and feet. They can significantly impact a person’s quality of life and overall health. Therefore, it is crucial to understand the types of complications that can occur and how to prevent them effectively.
What are diabetes complications?
Diabetes complications are the long-term consequences of having uncontrolled blood sugar levels over time. These complications can develop gradually and may include cardiovascular diseases, kidney problems, eye conditions, nerve damage, and foot complications. It is important to note that not everyone with diabetes will experience complications, especially if their condition is well-managed. However, it is essential to be aware of the potential risks and take proactive steps to prevent these complications from occurring.
Types of diabetes complications
- Cardiovascular complications: Chronic high blood sugar levels can lead to the development of heart disease, including coronary artery disease, heart attack, stroke, and peripheral artery disease.
- Kidney complications: Diabetes is one of the leading causes of kidney disease. High blood sugar levels can damage the kidneys, leading to diabetic nephropathy, a condition that impairs kidney function.
- Eye complications: Diabetes can affect the blood vessels in the eyes, leading to various eye conditions, including diabetic retinopathy, cataracts, and glaucoma.
- Nerve damage: High blood sugar levels can damage the nerves throughout the body, causing peripheral neuropathy, which often leads to numbness, tingling, pain, and problems with digestion, urination, and sexual function.
- Foot complications: Diabetes can impair blood flow to the feet and damage the nerves, increasing the risk of foot ulcers, infections, and, in severe cases, amputation.
Risk Factors for Diabetes Complications
While not everyone with diabetes will experience complications, certain risk factors increase the likelihood of developing them. It is important to be aware of these risk factors and take appropriate measures to mitigate their impact.
Uncontrolled blood sugar levels
The most significant risk factor for developing diabetes complications is uncontrolled blood sugar levels. Consistently elevated blood sugar levels contribute to the cumulative damage that can occur in various organs and systems in the body. Proper management of blood sugar through medication, diet, exercise, and regular monitoring is essential to minimize the risk and progression of complications.
High blood pressure and cholesterol
Individuals with diabetes are at an increased risk of high blood pressure and abnormal cholesterol levels, which further raise the risk of heart disease and stroke. Regular monitoring of blood pressure and cholesterol levels, along with lifestyle modifications and medications as prescribed by healthcare professionals, can help reduce the risk of complications.
Smoking
Smoking is detrimental to anyone’s health, but individuals with diabetes are particularly susceptible to its adverse effects. Smoking damages blood vessels, impairs circulation, and increases the risk of complications such as heart disease, stroke, and foot problems. Quitting smoking is crucial in preventing or mitigating further diabetes-related complications.
Obesity
Obesity is closely linked to the development of type 2 diabetes and increases the risk of complications. Excess body weight can contribute to insulin resistance, high blood pressure, and abnormal cholesterol levels. Managing a healthy weight through a balanced diet, regular physical activity, and lifestyle changes can aid in Preventing complications.
Lack of physical activity
Sedentary lifestyles can worsen insulin resistance, blood sugar control, and overall cardiovascular health. Regular physical activity helps improve blood sugar management, maintain a healthy weight, and reduce the risk of complications. Engaging in activities such as walking, swimming, cycling, or any form of exercise that suits an individual’s abilities and preferences is highly beneficial.
Genetics
While genetics play a role in the development of diabetes, they also influence an individual’s susceptibility to complications. Some people may have a genetic predisposition to certain complications, such as diabetic retinopathy or kidney disease. Understanding one’s genetic risk factors can prompt more targeted preventive measures and regular screenings.
Duration of diabetes
The longer a person has diabetes, the higher their risk of developing complications. Consistent management of blood sugar levels, blood pressure, and cholesterol becomes increasingly important as the duration of diabetes progresses. Regular healthcare check-ups and adherence to prescribed medications and lifestyle modifications are crucial to minimize the impact of long-standing diabetes.

Preventing Diabetes Complications
While the prospect of diabetes complications can be daunting, the good news is that many of them can be prevented or delayed with appropriate measures. By adopting a healthy lifestyle and actively managing diabetes, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of complications.
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle
Adopting and maintaining healthy habits is essential for preventing and managing diabetes complications. This includes consuming a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, getting enough sleep, managing stress, and avoiding excessive alcohol consumption.
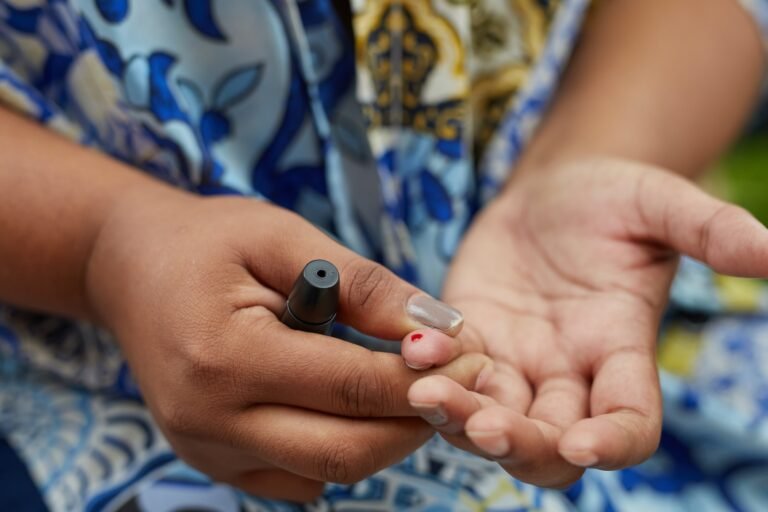
Regularly monitoring blood sugar levels
Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels is crucial for individuals with diabetes. This involves performing regular fingerstick glucose tests or using continuous glucose monitoring systems. By tracking blood sugar trends, individuals can make necessary adjustments to their diabetes management plan to maintain optimal control.
Managing blood pressure and cholesterol
Controlling blood pressure and cholesterol levels is vital for reducing the risk of cardiovascular complications. Along with lifestyle modifications such as healthy eating and regular exercise, medications prescribed by healthcare professionals may be necessary to maintain optimal levels.
Quitting smoking
Quitting smoking is crucial for individuals with diabetes due to the increased risk of complications associated with smoking. Seeking professional help, joining support groups, using nicotine replacement therapy, and implementing strategies to cope with cravings can greatly assist in successfully quitting smoking.
Maintaining a healthy weight
Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight is beneficial for overall diabetes management and prevention of complications. This can be accomplished through a combination of healthy eating, portion control, regular physical activity, and seeking guidance from healthcare professionals or registered dietitians.
Engaging in physical activity
Regular physical activity offers numerous benefits for individuals with diabetes, such as improved blood sugar control, weight management, cardiovascular health, and stress reduction. Finding enjoyable activities and incorporating them into daily routines can make it easier to maintain an active lifestyle.
Following a healthy diet
A healthy diet plays a crucial role in diabetes management and preventing complications. This includes consuming a variety of nutrient-rich foods, focusing on whole grains, lean proteins, fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats. Balancing carbohydrates, monitoring portion sizes, and minimizing the intake of processed foods and sugary beverages are essential.
Attending regular medical check-ups
Regular check-ups with healthcare professionals are essential for monitoring overall health, assessing risk factors, and detecting potential complications in their early stages. These check-ups may include blood tests, eye exams, foot examinations, and discussions about medications and lifestyle modifications.
Taking medications as prescribed
Strict adherence to prescribed medications is crucial for managing diabetes effectively. Medications such as insulin, oral glucose-lowering medications, blood pressure medications, and cholesterol-lowering drugs can greatly contribute to preventing complications. Following prescribed dosages, schedules, and any necessary adjustments is vital.
Ensuring good foot care
Proper foot care is vital for individuals with diabetes as damage to the feet can lead to serious complications. Daily foot care routines, including washing and thoroughly drying feet, inspecting for any cuts or sores, wearing proper footwear, and promptly seeking treatment for any issues, can minimize the risk of foot-related complications.
Controlling Blood Sugar Levels
Maintaining optimal blood sugar control is of paramount importance in diabetes management and preventing complications. Consistently high blood sugar levels significantly increase the risk of various complications. Therefore, understanding the importance of blood sugar control and adopting effective measures is crucial.
Importance of blood sugar control
Consistent blood sugar control is essential for preventing diabetes complications. High blood sugar levels over time can lead to damage in the blood vessels and nerves, contributing to complications such as heart disease, kidney problems, eye conditions, and nerve damage. Keen attention to blood sugar levels is necessary for overall health and well-being.
Monitoring blood sugar levels
Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels allows individuals to understand how their bodies respond to certain foods, physical activity, medications, and other factors that may influence blood sugar levels. This can be done through self-monitoring using fingerstick glucose tests or using continuous glucose monitoring systems.
Using insulin or diabetes medications
For individuals with type 1 diabetes or type 2 diabetes requiring insulin, proper administration of insulin is crucial for blood sugar control. In addition, individuals with type 2 diabetes may be prescribed oral glucose-lowering medications to enhance blood sugar management. Adhering to prescribed insulin regimens or medication schedules is essential to maintain optimal blood sugar control.
Following a diabetic meal plan
A diabetic meal plan, often developed with the guidance of a registered dietitian, serves as a framework for managing blood sugar levels through appropriate food choices and portion control. The plan typically emphasizes a balanced intake of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats in accordance with an individual’s specific needs.
Counting carbohydrates
Carbohydrate counting is a method used by individuals with diabetes to track their carbohydrate intake, as carbohydrates have the most significant impact on blood sugar levels. By understanding the carbohydrate content of various foods, individuals can make informed choices and better manage their blood sugar levels.
Balancing exercise with blood sugar management
Exercise has a direct impact on blood sugar levels, as physical activity can both lower blood sugar and increase sensitivity to insulin. Balancing exercise with blood sugar management involves monitoring blood sugar levels before, during, and after exercise, adjusting insulin or medication dosages as needed, and consuming appropriate snacks to prevent hypoglycemia.
Recognizing and managing hyperglycemia
Hyperglycemia, or high blood sugar, can occur for various reasons, such as inadequate insulin doses, illness, stress, or consuming high-carbohydrate meals. Recognizing the symptoms of hyperglycemia, such as increased thirst, frequent urination, fatigue, and blurred vision, and taking appropriate action, such as adjusting insulin doses or seeking medical advice, is crucial in controlling blood sugar levels.
Recognizing and managing hypoglycemia
Hypoglycemia, or low blood sugar, can pose immediate health risks and should be promptly addressed. symptoms of hypoglycemia may include shakiness, dizziness, confusion, sweating, and weakness. Individuals should keep a source of fast-acting carbohydrates on hand, such as glucose tablets or fruit juice, and promptly treat hypoglycemia to maintain blood sugar balance.
Managing Blood Pressure and Cholesterol
High blood pressure and abnormal cholesterol levels are common comorbidities among individuals with diabetes. Managing these conditions is essential to reduce the risk of cardiovascular complications and other related health issues.
The impact of high blood pressure and cholesterol
High blood pressure and abnormal cholesterol levels significantly increase the risk of heart disease, stroke, and other cardiovascular complications. Individuals with diabetes are already at higher risk for these conditions, making blood pressure and cholesterol management of utmost importance for overall health.
Lifestyle changes to lower blood pressure and cholesterol
Lifestyle modifications play a crucial role in managing blood pressure and cholesterol levels. These include adopting a healthy diet, reducing salt intake, increasing physical activity, quitting smoking, limiting alcohol consumption, managing stress, and maintaining a healthy weight. These changes can contribute to significant improvements in blood pressure and cholesterol control.
Medications for blood pressure and cholesterol
In cases where lifestyle modifications are insufficient in achieving optimal blood pressure and cholesterol levels, healthcare professionals may prescribe medications. These medications may include angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs), diuretics, beta-blockers, statins, or other drugs that effectively manage blood pressure and cholesterol levels.
Regular check-ups and monitoring
Regular check-ups with healthcare professionals are vital for monitoring blood pressure and cholesterol levels. These check-ups can help detect any abnormalities and allow healthcare professionals to make necessary adjustments to medications or lifestyle recommendations. Monitoring blood pressure and cholesterol at home may also be recommended for ongoing management.
Complications of uncontrolled blood pressure and cholesterol
Persistent high blood pressure and abnormal cholesterol levels can lead to various complications, including heart disease, heart attack, stroke, peripheral artery disease, and kidney problems. Complications can be severe and impact a person’s overall quality of life. Therefore, it is essential to actively manage blood pressure and cholesterol levels to minimize the risk of these adverse outcomes.
Smoking Cessation
Smoking poses significant risks to individuals with diabetes, further increasing their susceptibility to complications. Quitting smoking is a crucial step toward better health and preventing further harm.
Dangers of smoking for people with diabetes
Smoking is particularly detrimental to individuals with diabetes due to its adverse effects on blood vessels, circulation, and infection resistance. Smoking increases the risk of developing cardiovascular diseases, lung diseases, foot problems, and other complications associated with diabetes. Quitting smoking is therefore crucial in lowering these risks.
Benefits of quitting smoking
Quitting smoking offers numerous health benefits to individuals with diabetes. These benefits include improved blood circulation, reduced risk of heart disease and stroke, improved lung function, decreased risk of infections, better wound healing, and a higher overall quality of life. The sooner a person quits smoking, the greater the potential benefits.
Support and resources for quitting
Quitting smoking can be challenging, but various support systems and resources are available to assist individuals with diabetes in their journey toward a smoke-free life. These resources include healthcare professionals, smoking cessation programs, support groups, helplines, online forums, and educational materials. Taking advantage of these resources can greatly increase the chances of successfully quitting smoking.
Strategies for successful smoking cessation
Successful smoking cessation often involves a combination of strategies tailored to individual needs and preferences. These strategies may include setting a quit date, finding alternative coping mechanisms for stress, avoiding triggers, identifying support networks, using nicotine replacement therapy, and seeking professional guidance and counseling. Persistence, perseverance, and a positive mindset are also key in overcoming the challenges of quitting smoking.

Weight Management and Physical Activity
Obesity is closely linked to the development of type 2 diabetes and exacerbates the risk of complications. Managing a healthy weight and engaging in regular physical activity are vital for diabetes management and prevention of associated complications.
Link between obesity and diabetes complications
Obesity is a significant risk factor for developing type 2 diabetes, as excess body weight contributes to insulin resistance. In individuals who already have diabetes, obesity can worsen blood sugar control, increase the risk of cardiovascular diseases and other complications, and hinder overall disease management.
Setting weight loss goals
Setting realistic weight loss goals is important for individuals with diabetes. The goals should be achievable and sustainable, focusing on gradual weight loss rather than drastic changes. Losing as little as 5-10% of overall body weight can significantly improve blood sugar control and reduce the risk of complications.
Strategies for healthy weight loss
Healthy weight loss is achieved through a combination of dietary changes, increased physical activity, and adopting positive lifestyle habits. This may involve reducing calorie intake, choosing nutrient-dense foods, portion control, regular meal timing, mindful eating practices, and seeking guidance from healthcare professionals or registered dietitians.
Importance of physical activity for diabetes management
Physical activity plays a crucial role in diabetes management for individuals of all weight categories. Regular exercise enhances blood sugar control, improves insulin sensitivity, helps with weight management, reduces cardiovascular risks, and promotes overall well-being. Individuals should aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity per week, along with strength training exercises.
Choosing an exercise routine
When selecting an exercise routine, it is important to choose activities that are enjoyable, appropriate for fitness levels, and fit into one’s lifestyle. This can include activities such as walking, swimming, cycling, dancing, or engaging in sports. Additionally, incorporating both aerobic exercises and strength training exercises is beneficial for overall health and diabetes management.
Safety considerations for physical activity
Individuals with diabetes should take certain safety precautions before engaging in physical activity. This includes consulting with healthcare professionals to determine if any special precautions or modifications are necessary, monitoring blood sugar levels before and after exercise, staying hydrated, wearing appropriate footwear, and being mindful of any signs of hypoglycemia or other adverse effects during physical activity.
Incorporating exercise into daily life
Finding ways to incorporate physical activity into daily life can help individuals achieve regular exercise without disrupting their routine. This can include taking the stairs instead of the elevator, parking farther away, walking or biking to nearby destinations, doing household chores, or joining group activities or exercise classes. Making physical activity a priority and finding enjoyable ways to move more can lead to long-term adherence.
Healthy Eating for Diabetes
Diet plays a crucial role in diabetes management, blood sugar control, and prevention of complications. Adopting a healthy eating plan that focuses on nutrient-rich foods and proper portion control is key to maintaining optimal health.
Understanding the role of diet in diabetes management
Diet plays a vital role in managing blood sugar levels, achieving a healthy weight, and promoting overall health for individuals with diabetes. A balanced diet provides the necessary nutrients, vitamins, and minerals while controlling the intake of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins.
Balancing macronutrients
Balancing macronutrients in the diet is important for individuals with diabetes. This involves consuming carbohydrates, proteins, and fats in appropriate proportions to maintain blood sugar control and overall health. Portion control and choosing nutrient-dense options within each macronutrient group are vital.
Choosing low glycemic index foods
The glycemic index (GI) ranks foods based on how they affect blood sugar levels. Choosing low GI foods can help individuals with diabetes better manage their blood sugar levels. Foods with lower GI values, such as whole grains, legumes, non-starchy vegetables, and certain fruits, have a smaller impact on blood sugar compared to high GI foods like white bread, sugary drinks, and processed snacks.
Portion control and mindful eating
Portion control is crucial for individuals with diabetes, as it directly impacts blood sugar control and weight management. Measuring portion sizes, using smaller plates, eating slowly, and being mindful of hunger and fullness cues can help prevent overeating and maintain a healthy balance of food intake.
Meal planning and preparation
Meal planning and preparation can empower individuals with diabetes to make healthy food choices and control their blood sugar levels. Planning ahead, grocery shopping with a list, preparing balanced meals in advance, and packing healthy snacks all contribute to maintaining a consistent and nutritious diet.
Nutritional counseling and education
Seeking guidance from healthcare professionals or registered dietitians can provide valuable insights into proper nutrition for diabetes management. Nutritional counseling and education sessions can help individuals better understand their dietary needs, develop personalized meal plans, and learn effective strategies for making healthy choices and achieving long-term dietary changes.
Regular Medical Check-ups
Regular medical check-ups are a crucial aspect of diabetes management and preventive care. These check-ups allow healthcare professionals to assess overall health, monitor blood sugar control, and screen for potential complications.
Why regular check-ups are important
Regular check-ups are important because they provide an opportunity to assess the effectiveness of diabetes management, detect any potential problems, and make necessary adjustments to treatment plans. They also allow healthcare professionals to monitor blood pressure, cholesterol levels, kidney function, foot health, and other crucial aspects of diabetes care.
Recommended frequency of check-ups
The frequency of medical check-ups may vary depending on individual circumstances, but it is generally recommended for individuals with diabetes to undergo comprehensive assessments at least once a year. Additional check-ups, such as quarterly or biannual visits, may be necessary for individuals with specific needs or risk factors.
Assessing risk factors and complication screenings
Regular check-ups include assessments of various risk factors and screenings for potential complications. These may include blood tests to monitor blood sugar levels, HbA1c tests to assess long-term blood sugar control, lipid profiles to check cholesterol levels, urine tests to evaluate kidney function, eye exams to assess for diabetic retinopathy, and foot exams to identify any signs of complications.
Collaborating with healthcare professionals
Active collaboration with healthcare professionals is essential for effective diabetes management. Regular check-ups provide an opportunity to discuss any concerns or challenges, seek guidance on medication adjustments, receive education on lifestyle modifications, and develop personalized care plans based on individual needs and goals.
Maintaining a diabetes management schedule
Maintaining a diabetes management schedule is vital for overall health. This involves adhering to the recommended frequency of check-ups, blood sugar monitoring, medication routines, exercise regimens, and meal planning. By establishing a routine and staying organized, individuals can stay proactive in their diabetes care and prevent potential complications.
Foot Care for Diabetes
Foot care is a critical aspect of diabetes management, as diabetes can impair blood flow and damage nerves in the feet, leading to serious complications. Proper foot care routines and regular podiatry visits are essential for preventing foot-related complications.
Why foot care is important for people with diabetes
People with diabetes are at a higher risk of developing foot problems due to impaired circulation and nerve damage. Proper foot care is essential to prevent complications such as foot ulcers, infections, and, in severe cases, amputations. Good foot health contributes to overall mobility, comfort, and well-being.
Daily foot care routine
A daily foot care routine is essential for individuals with diabetes and should include several key steps. These may include washing and thoroughly drying the feet, inspecting the feet for any cuts, sores, or changes in color or temperature, moisturizing the feet to prevent dry skin, and regularly trimming nails to avoid ingrown nails.
Checking for signs of complications
Regular foot inspections are crucial for identifying any signs of complications. This includes checking for blisters, cuts, calluses, redness, swelling, or other abnormalities. Early detection enables prompt treatment and prevents the progression of foot-related complications.
Proper footwear and socks
Choosing proper footwear is vital for individuals with diabetes. Well-fitting shoes that provide adequate support, protection, and cushioning help prevent injuries and pressure points. Additionally, wearing moisture-wicking socks that reduce friction and keep the feet dry is beneficial for overall foot health.
Regular podiatry visits
Regular visits to a podiatrist, or foot specialist, are an essential part of foot care for individuals with diabetes. Podiatrists can conduct comprehensive foot examinations, identify any potential issues, provide necessary treatments such as nail trimming or callus removal, and offer valuable guidance on footwear and foot care practices tailored to individual needs.
Managing foot ulcers and infections
If foot ulcers or infections develop, prompt medical attention is crucial. Individuals should seek immediate treatment from healthcare professionals to prevent the spread of infection and potential foot complications. Adhering to prescribed treatments and following recommended wound care practices are instrumental in promoting healing and preventing further issues.
In conclusion, while diabetes complications can be concerning, they are not inevitable. By prioritizing optimal blood sugar control, managing blood pressure and cholesterol levels, adopting healthy lifestyle habits, and actively engaging in preventive care, individuals with diabetes can significantly reduce their risk of complications. Regular check-ups, adhering to prescribed medications and treatments, and seeking professional guidance when necessary are essential in maintaining healthy living with diabetes. By implementing appropriate strategies and making conscious efforts in diabetes management, individuals can lead fulfilling lives while minimizing the impact of complications.