Understanding the Inevitable Complications of Diabetes
Diabetes, a chronic condition characterized by high blood sugar levels, affects millions of people worldwide. Inevitably, this condition can lead to various complications that can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life. From eye problems and nerve damage to heart disease and kidney issues, the complications associated with diabetes are both numerous and severe. Understanding these inevitable complications is crucial for both individuals living with diabetes and their loved ones, as it allows them to take proactive measures to mitigate the risks and ensure a healthier future.
Table of Contents
Understanding the Inevitable Complications of Diabetes
Introduction
Diabetes is a prevalent chronic condition that affects millions of people worldwide. While it can be managed through proper medical care and lifestyle choices, there are inevitable complications that can arise from this condition. Understanding these complications is crucial for both individuals living with diabetes and their loved ones, as it can help them be proactive in preventing and minimizing the risks associated with the disease.
What is Diabetes?
Diabetes is a metabolic disorder characterized by high levels of glucose in the blood. It occurs when the body either doesn’t produce enough insulin, a hormone responsible for regulating blood sugar, or when the body is unable to use insulin effectively. This results in an imbalance of blood sugar levels, leading to various health complications.
Types of Diabetes
There are different types of diabetes, with the most common ones being type 1 and type 2 diabetes. Type 1 diabetes usually develops during childhood or adolescence and is characterized by the body’s inability to produce insulin. On the other hand, type 2 diabetes typically occurs in adulthood and is primarily caused by insulin resistance, where the body cannot use insulin effectively. There are also other types, such as gestational diabetes, which occurs during pregnancy.
Causes of Diabetes
The exact causes of diabetes vary depending on the type. Type 1 diabetes is believed to be an autoimmune disease, where the body’s immune system attacks and destroys the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. Type 2 diabetes is primarily caused by a combination of genetic factors and lifestyle choices, such as obesity, lack of physical activity, and poor diet. Gestational diabetes is caused by hormonal changes during pregnancy, which can affect insulin production and utilization.
Managing Diabetes
While diabetes is a chronic condition that requires lifelong management, it can be effectively controlled through various methods. Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels, taking prescribed medications, and incorporating lifestyle modifications are crucial in managing the disease. By adopting a healthy lifestyle, individuals can keep their blood sugar levels within a target range and reduce the risk of complications.
Impact of Diabetes
Diabetes can have a significant impact on an individual’s health and overall well-being. It affects multiple organs and systems in the body, leading to various complications. These complications can range from mild to severe, but they are not entirely avoidable. However, with proper management, individuals can reduce their impact and improve their quality of life.
Common Diabetes Complications
Diabetes complications can affect different parts of the body, including the eyes, nerves, cardiovascular system, kidneys, skin, gastrointestinal system, feet, mental health, and even pregnancy. Each complication poses its own set of challenges and requires specialized care to prevent further deterioration. Some of the common complications associated with diabetes include:
Eye Complications
People with diabetes are at a higher risk of developing eye complications, such as diabetic retinopathy, cataracts, and glaucoma. Diabetic retinopathy, in particular, is a leading cause of blindness among adults. It occurs when high blood sugar levels damage the blood vessels in the retina, leading to vision loss if left untreated. Regular eye exams and proper management of diabetes can help minimize the risk of such complications.
Neuropathy
Diabetic neuropathy refers to nerve damage caused by high blood sugar levels over time. It commonly affects the peripheral nerves, leading to symptoms like numbness, tingling, and pain in the hands and feet. Neuropathy can also affect other parts of the body, including the digestive system and the heart. Proper blood sugar control, along with medications and lifestyle modifications, is essential in managing neuropathy.
Cardiovascular Complications
Diabetes significantly increases the risk of cardiovascular diseases, including heart attacks, strokes, and peripheral artery disease. High blood sugar levels, combined with other risk factors such as high blood pressure and high cholesterol, contribute to the development of these complications. Adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise, a balanced diet, and cholesterol-lowering medications if necessary, can help in preventing cardiovascular complications.
Kidney Damage
Diabetic nephropathy, or kidney damage, is a common complication of diabetes. It occurs when high blood sugar levels damage the tiny blood vessels in the kidneys, impairing their ability to filter waste and excess fluid effectively. This can lead to chronic kidney disease and, in severe cases, kidney failure. Close monitoring of blood pressure, blood sugar levels, and regular check-ups with a healthcare provider can help in managing kidney complications.
Skin Complications
People with diabetes are more prone to various skin conditions, including bacterial and fungal infections, dry skin, slow-healing wounds, and diabetic dermopathy. High blood sugar levels can affect the skin’s ability to heal, making individuals vulnerable to infections and other skin problems. Maintaining good hygiene, moisturizing the skin, and promptly treating any wounds or infections are essential in preventing and managing skin complications.
Gastroparesis
Gastroparesis is a condition that affects the digestive system, causing delayed emptying of the stomach. It occurs when high blood sugar levels damage the nerves that control the muscles in the stomach, leading to symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, bloating, and stomach pain. Managing blood sugar levels, dietary modifications, and medications are crucial in alleviating the symptoms and preventing complications associated with gastroparesis.
Foot Complications
Diabetes can cause foot complications, such as neuropathy and poor circulation, leading to an increased risk of foot ulcers, infections, and even amputations. Regular foot care, including daily inspections, proper hygiene, wearing comfortable footwear, and regular check-ups with a podiatrist, can help in preventing and minimizing foot complications.
Mental Health Challenges
Living with diabetes can take a toll on an individual’s mental health. The constant need to monitor blood sugar levels, follow a strict regimen, and deal with the potential complications can lead to stress, anxiety, and depression. It is essential to address these mental health challenges by seeking support from healthcare professionals, joining support groups, and practicing self-care techniques, such as meditation and mindfulness.

Complications during Pregnancy
Pregnant women with diabetes face additional challenges in managing their condition. Poorly controlled blood sugar levels during pregnancy can lead to complications for both the mother and the baby. These complications may include preeclampsia, preterm birth, birth defects, and a higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life. Close monitoring, regular prenatal care, and proper management of blood sugar levels are vital in minimizing the risks associated with diabetes during pregnancy.
Hypoglycemia and Hyperglycemia
Both hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) and hyperglycemia (high blood sugar) can occur as a result of diabetes management. Hypoglycemia can cause symptoms like dizziness, confusion, and even loss of consciousness, while hyperglycemia can lead to increased thirst, frequent urination, and fatigue. Recognizing the symptoms and taking prompt action, such as consuming glucose tablets for hypoglycemia or adjusting insulin doses for hyperglycemia, is crucial in preventing complications.
Preventing and Minimizing Complications
While diabetes complications may be inevitable to some extent, there are steps individuals can take to reduce their impact and improve their overall health.
Importance of Regular Check-ups
Regular check-ups with healthcare professionals, including primary care physicians, endocrinologists, ophthalmologists, podiatrists, and other specialists, are essential in monitoring and managing diabetes complications. These healthcare providers can help identify any emerging issues, adjust treatment plans, and provide personalized guidance for optimal diabetes care.
Maintaining a Healthy Lifestyle
adopting a healthy lifestyle is crucial in minimizing the risks associated with diabetes complications. This includes maintaining a healthy body weight, following a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and avoiding tobacco and excessive alcohol consumption. These lifestyle choices can contribute to better blood sugar control, improved cardiovascular health, and overall well-being.
Adopting a Balanced Diet
A balanced diet plays a vital role in managing diabetes and reducing the risk of complications. The focus should be on consuming nutrient-dense foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Limiting the intake of processed foods, sugary beverages, and foods high in saturated and trans fats is crucial for maintaining stable blood sugar levels and overall health.
Exercising Regularly
Physical activity is not only beneficial for managing weight but also for maintaining healthy blood sugar levels and reducing the risk of diabetes complications. Engaging in regular exercise, such as walking, cycling, swimming, or any other form of aerobic activity, can help improve insulin sensitivity, lower blood pressure, and promote cardiovascular health. It is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new exercise regimen.
Managing Stress
Stress can affect blood sugar levels and overall health, making stress management an important aspect of diabetes care. Engaging in stress-reducing activities, such as deep breathing exercises, yoga, meditation, or engaging in hobbies, can help individuals better cope with the challenges of living with diabetes and minimize the impact on their health.
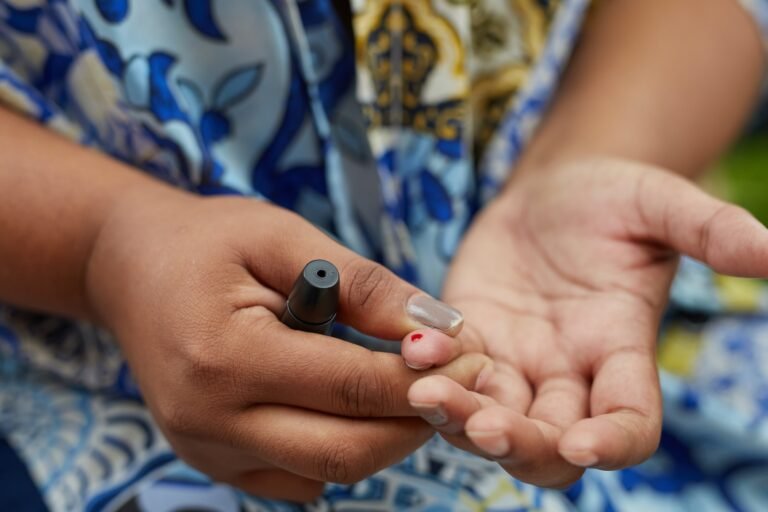
Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels
Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels is crucial in diabetes management to prevent complications. This allows individuals to make necessary adjustments to their medication regimen, dietary choices, and activity levels. Frequent monitoring also helps identify patterns and trends, enabling better blood sugar control and minimizing the risks associated with high or low blood sugar levels.
Conclusion
While diabetes complications may be inevitable to some degree, understanding and actively managing the disease can significantly reduce their impact on an individual’s health and well-being. By adopting a proactive approach, adhering to a healthy lifestyle, and seeking regular medical care, individuals with diabetes can minimize the risks associated with complications and lead fulfilling lives. Education and support play vital roles in ensuring the best possible outcomes for those affected by diabetes, empowering them to take charge of their health and effectively manage their condition.